Tornado Tracking and Prediction: Tornado Tracker
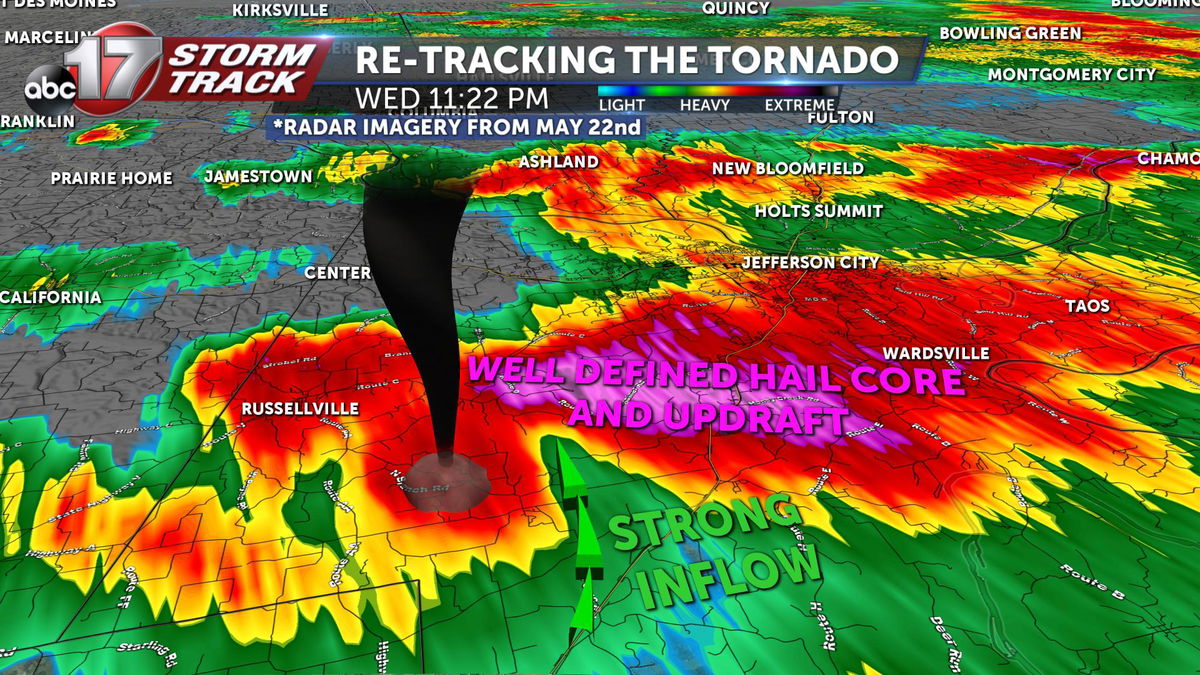
Tornado tracker – Tornadoes, violent and unpredictable storms, pose a significant threat to communities worldwide. Tracking and predicting these tornadoes is crucial for issuing timely warnings and implementing safety measures. This article delves into the principles, technologies, and challenges involved in tornado tracking and prediction.
Amidst the tumultuous skies, tornado trackers vigilantly monitor the dance of nature’s fury. Their keen eyes scan the horizon, anticipating the slightest hint of a swirling vortex. As the storm approaches, they navigate the intricate tapestry of tyler tx weather , analyzing its every nuance.
With each passing moment, the trackers refine their predictions, guiding those in harm’s way towards safety.
Methods of Tornado Tracking
- Doppler Radar: Doppler radar emits radio waves that bounce off objects and return to the radar receiver. By analyzing the changes in the frequency of the reflected waves, meteorologists can determine the velocity and direction of wind currents, including those associated with tornadoes.
- Spotter Networks: Trained spotters, often volunteers, observe and report tornado sightings to weather authorities. Their observations provide valuable ground-level information, complementing radar data.
- Satellite Imagery: Satellite images can detect tornado-producing supercell thunderstorms based on their characteristic cloud patterns and atmospheric conditions.
Technologies for Tornado Detection and Prediction
- Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) Models: NWP models are computer simulations that forecast weather patterns. By incorporating data from weather stations, satellites, and other sources, these models can predict the likelihood and location of tornado-producing storms.
- Mesoscale Analysis and Prediction System (MAPS): MAPS is a real-time data analysis and forecasting system that combines radar, satellite, and other data to provide detailed forecasts of severe weather, including tornadoes.
- Warn-on-Forecast (WoF) Systems: WoF systems use NWP models and other data to issue warnings for specific areas where tornadoes are predicted to occur.
Challenges and Limitations of Tornado Tracking Systems
Despite significant advancements, tornado tracking and prediction systems face challenges:
- Data Limitations: Radar and other detection methods may have blind spots or limitations in detecting tornadoes, especially in areas with complex terrain or heavy precipitation.
- False Positives: Warning systems can sometimes issue false alarms, leading to unnecessary evacuations or anxiety.
- Short Lead Times: Tornadoes can form and intensify rapidly, leaving limited time for warnings and response.
Tornado Safety and Preparedness

In the face of the destructive force of tornadoes, it is imperative for individuals and communities to be equipped with comprehensive safety measures and preparedness plans. By understanding the dynamics of these formidable storms, we can mitigate their impact and protect lives.
Early Warning Systems, Tornado tracker
Early warning systems play a crucial role in reducing tornado-related fatalities and injuries. Advanced radar technology and weather forecasting models enable meteorologists to detect and predict tornadoes with increasing accuracy. These systems provide valuable lead time for communities to issue warnings, allowing residents to seek shelter and take necessary precautions.
- Doppler radar detects changes in wind speed and direction, providing real-time information about the movement and intensity of tornadoes.
- Weather satellites monitor cloud formations and atmospheric conditions, identifying potential tornado-producing thunderstorms.
- Weather spotters report tornado sightings and provide ground-level observations to supplement radar data.
Tornado Climatology and Research
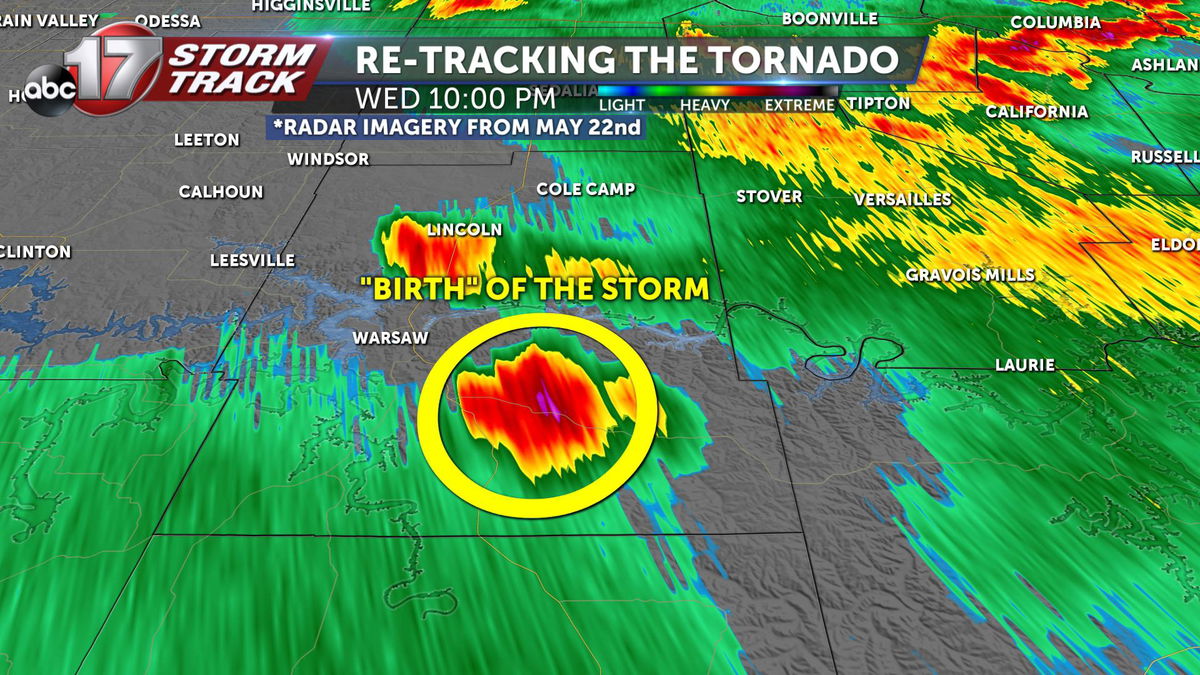
Understanding the patterns and dynamics of tornadoes is crucial for improving forecasting and mitigation strategies. Historical tornado data analysis helps identify high-risk areas and seasonal trends.
Factors Contributing to Tornado Formation and Intensity
- Wind Shear: Variations in wind speed and direction at different altitudes contribute to the formation of rotating updrafts, essential for tornado development.
- Instability: The presence of warm, moist air near the surface and cold, dry air aloft creates atmospheric instability, providing the energy source for tornadoes.
- Lift: Updrafts caused by factors such as heating, convergence, or terrain features initiate the lifting of air parcels, potentially leading to tornado formation.
Ongoing Research in Tornado Forecasting and Mitigation
Research efforts focus on improving tornado forecasting accuracy, including:
- Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) Models: Advancements in NWP models allow for more accurate simulations of atmospheric conditions that favor tornado development.
- Doppler Radar Observations: Real-time Doppler radar data provides valuable information on tornado rotation and wind speeds, aiding in timely warnings.
- Storm Chasing and Data Collection: Field campaigns gather data on tornado behavior and the surrounding environment, enhancing our understanding of these storms.
Mitigation strategies aim to reduce tornado damage and loss of life:
- Tornado-Resistant Building Codes: Enforcing building codes that mandate stronger structures can minimize the impact of tornadoes on infrastructure.
- Public Education and Awareness: Educating communities about tornado safety measures, such as seeking shelter in sturdy buildings or underground, helps reduce casualties.
- Tornado Warning Systems: Advanced warning systems provide timely alerts to communities in the path of a tornado, allowing for protective action.
As a tornado tracker, I’m attuned to the capricious dance of the elements. Yet, when the news of Hurricane Beryl reached me, I couldn’t help but be drawn to its path. It’s a reminder that nature’s wrath knows no boundaries, and that even in the midst of our scientific pursuits, we must remain vigilant in the face of its untamed power.